Biotin, also known as vitamin B7 or vitamin H, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including metabolism, maintaining healthy skin, hair, and nails, and supporting the nervous system.
This article explores the recommended daily biotin intake, its benefits, sources, and tips for ensuring adequate biotin levels.
Key Functions of Biotin
Biotin is essential for several important functions in the body:
Metabolism Support
Biotin acts as a coenzyme in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, helping to convert food into energy.
Healthy Skin, Hair, and Nails
Biotin supports the health of skin, hair, and nails. It is often included in beauty supplements to promote growth and strength.
Nervous System Function
Biotin is important for the proper functioning of the nervous system, aiding in nerve signaling and maintaining brain health.
Gene Regulation
Biotin plays a role in gene expression by helping to regulate the synthesis of certain proteins.
Recommended Daily Biotin Intake
The recommended daily intake of biotin varies based on age, gender, and life stage. Here are the guidelines provided by the National Institutes of Health (NIH):
Infants and Children
- 0-6 months: 5 micrograms (mcg)
- 7-12 months: 6 mcg
- 1-3 years: 8 mcg
- 4-8 years: 12 mcg
- 9-13 years: 20 mcg
Adolescents and Adults
- 14-18 years: 25 mcg
- 19 years and older: 30 mcg
Pregnant and Lactating Women
- Pregnant women: 30 mcg
- Lactating women: 35 mcg
Chart of Daily Biotin Requirements
| Age Group | Biotin Requirement (mcg/day) |
|---|---|
| Infants and Children | |
| 0-6 months | 5 |
| 7-12 months | 6 |
| 1-3 years | 8 |
| 4-8 years | 12 |
| 9-13 years | 20 |
| Adolescents and Adults | |
| 14-18 years | 25 |
| 19 years and older | 30 |
| Pregnant Women | 30 |
| Lactating Women | 35 |
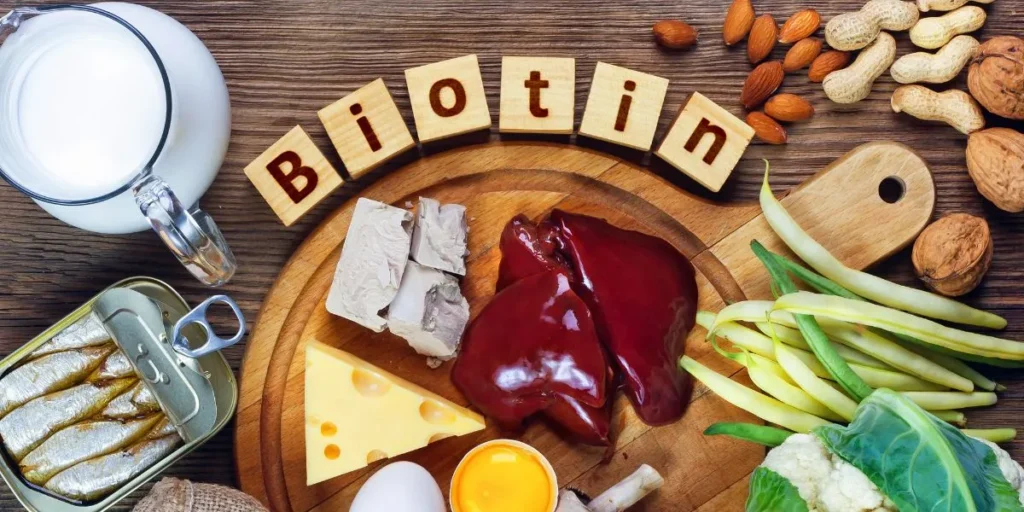
Sources of Biotin
Biotin is found in a variety of foods, making it possible to meet your daily requirements through a balanced diet. Here are some of the best dietary sources of biotin:
Animal Products
- Eggs: One cooked egg yolk provides about 10 mcg of biotin.
- Liver: A 3-ounce serving of cooked beef liver contains approximately 30 mcg of biotin.
- Fish: Salmon and tuna are good sources. A 3-ounce serving of cooked salmon offers around 5 mcg of biotin.
Plant-Based Sources
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, peanuts, and sunflower seeds are rich in biotin. An ounce of roasted almonds contains about 1.5 mcg of biotin.
- Legumes: Soybeans, peanuts, and peas provide biotin. A cup of cooked soybeans offers around 19 mcg of biotin.
- Whole Grains: Oats, barley, and wheat germ are good sources. A cup of cooked oatmeal contains about 0.2 mcg of biotin.
Vegetables and Fruits
- Sweet Potatoes: One medium sweet potato provides about 2.4 mcg of biotin.
- Spinach: A cup of raw spinach contains around 0.5 mcg of biotin.
- Bananas: One medium banana offers approximately 0.2 mcg of biotin.
Health Benefits of Biotin
Adequate biotin intake can provide numerous health benefits, including:
Improved Metabolism
Biotin supports the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, helping to convert food into energy and maintain overall metabolic health.
Healthier Skin, Hair, and Nails
Biotin is often included in beauty supplements due to its role in promoting healthy skin, hair, and nails. It can help prevent brittle nails, hair loss, and skin rashes.
Enhanced Brain Function
Biotin supports the proper functioning of the nervous system and brain health, potentially improving cognitive function and reducing the risk of neurological disorders.
Regulation of Blood Sugar Levels
Biotin may help regulate blood sugar levels by enhancing insulin sensitivity, making it beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
Tips to Increase Biotin Intake
Increasing your biotin intake can be achieved by making simple dietary changes. Here are some practical tips:
Include Biotin-Rich Foods
Incorporate foods high in biotin, such as eggs, liver, nuts, seeds, legumes, whole grains, and vegetables, into your daily meals.
Use Biotin Supplements
Consider taking biotin supplements if you have difficulty meeting your biotin needs through diet alone. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Cook Foods Properly
Avoid overcooking biotin-rich foods, as excessive heat can destroy biotin. Opt for steaming or lightly sautéing vegetables to preserve their nutrient content.
Eat a Balanced Diet
Ensure you consume a balanced diet that includes a variety of foods to obtain not only biotin but also other essential nutrients.
Monitoring Biotin Levels
It is important to monitor your biotin intake, especially if you have certain health conditions or dietary restrictions. Here are some key points to consider:
High Biotin Intake
Excessive biotin intake from supplements is generally considered safe, as biotin is water-soluble and excess amounts are excreted in urine. However, extremely high doses can interfere with certain laboratory tests, so it is important to follow recommended guidelines and consult with a healthcare provider.
Low Biotin Levels (Biotin Deficiency)
Biotin deficiency is rare but can occur due to inadequate dietary intake, genetic disorders, or certain medical conditions. Symptoms include thinning hair, brittle nails, skin rashes, and neurological issues. Increasing biotin intake through diet or supplements can help address deficiency.
Biotin Supplements
While it is generally best to obtain biotin from food sources, supplements may be necessary for some individuals, particularly those with dietary restrictions or increased biotin needs. Biotin supplements are available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and gummies. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best option for you.
FAQs
1. What is biotin?
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7 or vitamin H, is a water-soluble vitamin essential for metabolism, maintaining healthy skin, hair, and nails, and supporting the nervous system.
2. Why is biotin important?
Biotin is crucial for converting food into energy, supporting healthy skin, hair, and nails, maintaining proper nervous system function, and regulating gene expression.
3. How much biotin do I need per day?
The recommended daily intake of biotin varies by age, gender, and life stage. For adults, the recommendation is 30 mcg per day, with higher needs for pregnant and lactating women.
4. What are the best sources of biotin?
Foods rich in biotin include eggs, liver, nuts, seeds, legumes, whole grains, sweet potatoes, spinach, and bananas.
5. Can I get too much biotin?
Excessive biotin intake from supplements is generally considered safe, as biotin is water-soluble and excess amounts are excreted in urine. However, extremely high doses can interfere with certain laboratory tests.
6. Can I take biotin supplements?
Biotin supplements can be beneficial for individuals with dietary restrictions or increased biotin needs. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best supplementation option.
7. What are the symptoms of low biotin levels?
Symptoms of biotin deficiency include thinning hair, brittle nails, skin rashes, and neurological issues. Increasing biotin intake through diet or supplements can help address deficiency.
8. How can I increase my biotin intake?
You can increase your biotin intake by incorporating biotin-rich foods into your diet, considering biotin supplements, cooking foods properly, and eating a balanced diet.
9. Are biotin supplements necessary?
Biotin supplements may be necessary for individuals who have difficulty meeting their biotin needs through diet alone. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
10. How does biotin support skin, hair, and nail health?
Biotin promotes the production of keratin, a protein that supports the structure of skin, hair, and nails, helping to prevent brittleness and promote growth.
Conclusion
Biotin is an essential vitamin that supports many critical bodily functions, including metabolism, maintaining healthy skin, hair, and nails, and supporting the nervous system.
The recommended daily intake of biotin varies by age, gender, and life stage, with adults generally needing 30 mcg per day.
Ensuring adequate biotin intake through a balanced diet rich in biotin-containing foods or supplements can help maintain optimal health.
Always consult with a healthcare provider before taking biotin supplements, especially if you have health conditions that affect biotin levels.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure you get the right amount of biotin to support your overall well-being.
